Product Development Life Cycle: What it Is & How to Implement
Explore the key stages of the product development life cycle, from ideation to launch. Get valuable tips and insights for a successful product journey.
Posted March 6, 2025
Table of Contents
The product development life cycle is a structured framework that guides the transformation of an idea into a successful, market-ready product. This process is essential for companies looking to innovate and bring new offerings to consumers, ensuring that each step—from concept and design to production and launch—is carefully managed. Whether you are an entrepreneur or a seasoned business professional, a thorough understanding of this life cycle is vital for navigating the complexities of product development and achieving success in the marketplace. This guide will provide a detailed overview of each stage in the process and its importance in bringing products to fruition.
In this guide, you'll get a complete breakdown of the product development life cycle stages. We'll explore the different phases that make up this cycle, from the initial spark of an idea to the final product launch. You'll learn about effective strategies to put these stages into action, helping you navigate the challenges of product creation. Whether you're working on a new product design or looking to improve your current development process, this article will give you the insights you need to succeed in today's competitive market.
What Is the Product Development Life Cycle?
The product development life cycle is a systematic framework that enables companies to transform innovative concepts into commercially successful products.
It covers the entire journey from initial concept to market launch and beyond. This structured approach helps businesses manage the complex task of bringing new products to life while minimizing risks and maximizing the chances of market success.
At its core, the product development life cycle is about creating value for customers and businesses alike. It ensures that products meet customer needs, are developed within time and budget constraints, and align with overall business strategies. By breaking down the process into distinct phases, companies can coordinate efforts across different teams, allocate resources effectively, and make informed decisions at each stage of development.
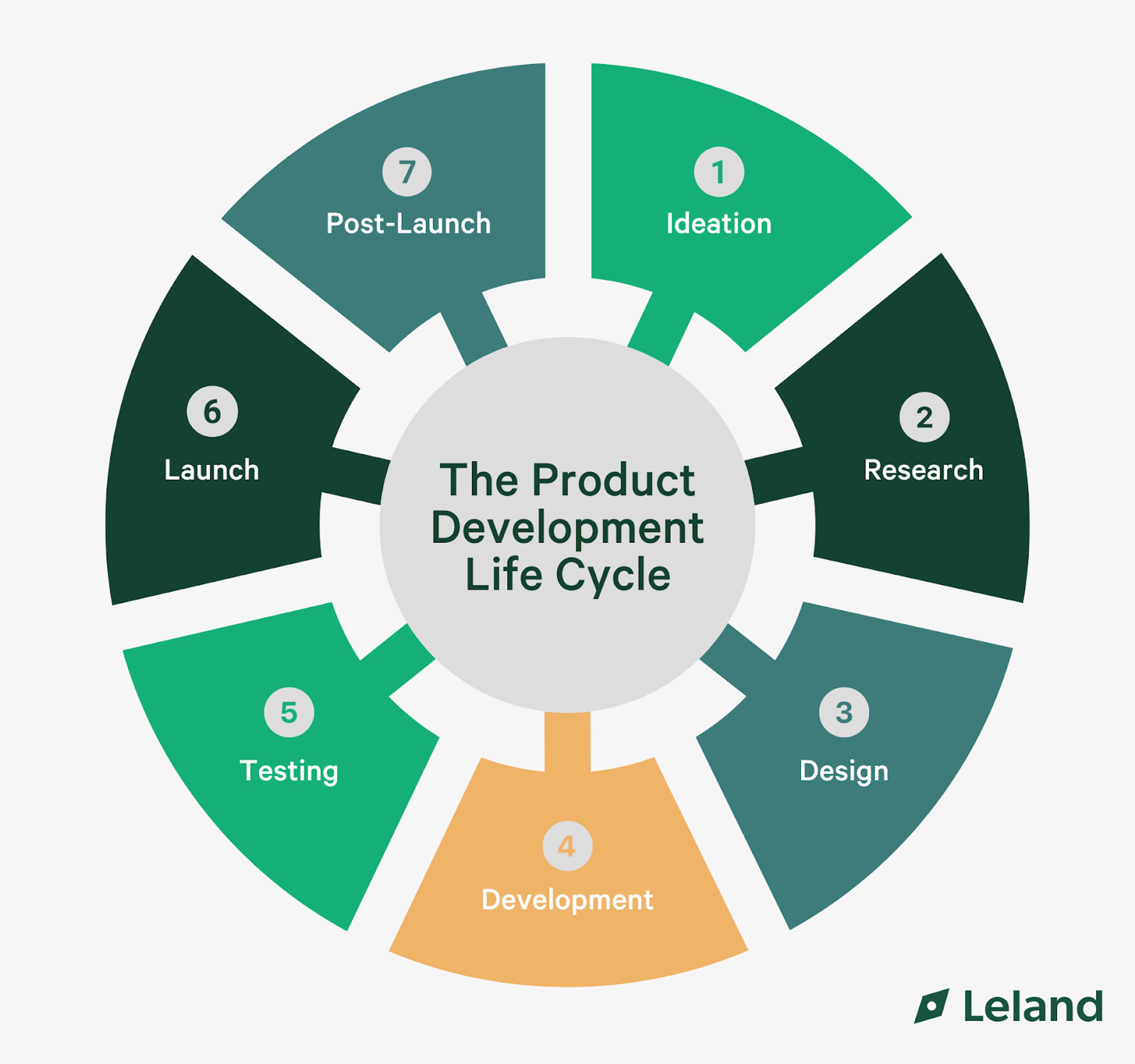
The 7 Stages of the Product Development Life Cycle
There is no universal agreement on the exact number of stages in the product development cycle. However, most models include the following seven key phases:
1. Ideation: This initial stage involves generating and evaluating new product ideas based on market research, customer needs, and business goals. The ideation phase often includes brainstorming sessions and analysis of customer pain points to ensure relevance to potential customers. During this phase, the product development process describes the creation of numerous concepts, from which the most promising ideas are selected. A critical part of ideation is defining the minimum viable product (MVP), which helps focus efforts on core features.
2. Concept Development: Here, promising ideas are further refined, and their viability is assessed through market analysis and feedback. The concept is expanded to include details like target market, key benefits, and differentiators. Design and development teams collaborate to create preliminary plans, ensuring the concept aligns with business goals. At this stage, feedback from potential customers is crucial to validate demand and shape the direction of the product.
3. Design: This phase focuses on creating detailed product specifications and building initial prototypes for testing and refinement. Design and development teams work closely to bring the concept to life, making decisions about product features and user interface. Prototypes are tested internally to identify issues and optimize functionality. The MVP is also considered here, allowing the team to focus on what’s necessary for early market validation without unnecessary features.
Also read: MVP vs. Prototype: What's the Difference and Which One Should You Use? | Leland
4. Development: The actual product is built during this stage, often using an iterative approach to incorporate feedback and improvements. Design and development teams work through sprints, continuously testing and refining product components. The focus is on ensuring all elements meet quality standards, with adjustments made as needed based on ongoing evaluations. The development of the MVP is a critical milestone, enabling the marketing team to prepare for a preliminary market introduction.
5. Testing: Rigorous testing is conducted to ensure the product meets quality standards and fulfills customer requirements. This includes functional testing, usability testing, and beta testing with a select group of potential customers. Feedback from these tests is used to make final refinements before launch. The product development process describes this stage as essential to guaranteeing a smooth user experience and identifying any last-minute issues.
6. Launch: The product is introduced to the market, supported by marketing and sales efforts. The marketing team plays a vital role in communicating the product's value, developing campaigns that reach the target audience. Launch strategies often include a focus on the MVP to gather early feedback. The commercialization phase also includes distribution planning, sales training, and public relations activities to maximize product awareness and adoption.
7. Post-Launch: After launch, companies gather feedback and data to make ongoing improvements and inform future product development cycles. This phase involves analyzing user feedback, market reception, and performance metrics to identify areas for enhancement. Continuous improvement is vital for extending the product life cycle and maintaining relevance in the market. Design and development teams collaborate to implement changes that enhance user satisfaction and keep the product competitive.
Benefits of Using the Product Development Lifecycle
- Faster Time-to-Market: By streamlining the development process, companies can bring products to market more quickly, capitalizing on time-sensitive opportunities.
- Improved Product Quality: A systematic approach ensures thorough testing and validation, resulting in higher-quality products that better meet customer needs.
- Risk Reduction: By breaking down the process into manageable stages, businesses can identify and address potential issues early, reducing the risk of costly mistakes.
- Enhanced Innovation: The structured approach encourages creative thinking and problem-solving at each stage, fostering a culture of innovation within the organization.
- Better Resource Allocation: Clear stages and milestones allow for more effective planning and allocation of time, money, and human resources.
- Improved Collaboration: The product development life cycle provides a framework for cross-functional teamwork, breaking down silos and enhancing communication across departments.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: By incorporating customer feedback and market data throughout the process, companies can make more informed decisions about product features and positioning.
For more resources on product development, see:
- Product Development Interview Questions: How to Prepare and Succeed | Leland
- The Different Phases of Product Development and How to Navigate Them | Leland
Product Lifecycle: Step-by-Step Breakdown
Stage 1 – Develop the idea
The product development life cycle kicks off with the ideation and concept development stage. This crucial phase involves generating and refining ideas for new products or features. To get the most out of this stage, it's essential to have a deep understanding of the problem you're trying to solve. This means conducting thorough market research, analyzing user feedback, and gathering input from all stakeholders involved.
During ideation, you'll want to encourage creativity and open-mindedness while remaining grounded in reality. Consider the resources and budget available for development, as well as any technical limitations that may occur. To narrow down the list of ideas, you can use efficient methods such as SWOT analysis or the SCAMPER technique. These approaches help make informed decisions and select the best options.
Once you've settled on a product idea, it's time to move on to building a prototype. This preliminary model showcases the primary solutions you plan to offer without any additional features. Creating a prototype is an excellent opportunity to get early feedback from internal and external users. Asking open questions about the product's design and expected functionality can help you gain valuable insights about where to move further with the MVP design.
Stage 2 – Research and validate the idea
Market research and validation are critical components of the product development life cycle. This stage involves conducting in-depth research and analysis on the selected product ideas to understand customer needs, market opportunities, competitive landscape, technical feasibility, and financial viability of the product.
To validate your product concept, consider documenting ideas in the form of a business case. This will allow all team members to have a clear understanding of the initial product features and the objectives of the new product launch. You'll want to include elements such as an executive summary, market analysis, competitive analysis, technical feasibility section, financial visibility, product scope, risk analysis, and a conclusion summarizing the main findings.
During this stage, it's crucial to define your target segment and create customer personas that form the foundation for the product. This includes meticulously examining market dynamics through comprehensive market research and analyzing factors such as market size, growth trends, drivers, barriers, regulations, and overall market dynamics.
Stage 3 – Design the prototype
Once you've validated your product concept, it's time to move on to the design and prototyping phase. This stage focuses on creating detailed product specifications and building initial prototypes for testing and refinement. The goal is to transform your idea into a tangible product that meets customer needs and aligns with your business objectives.
During this phase, you'll want to create a product vision statement – a comprehensive narrative delineating the purpose, value proposition, target market, and overarching goals of the forthcoming product. Following this, a product roadmap should be meticulously crafted, outlining the high-level plan, timeline, milestones, deliverables, dependencies, and necessary resources for the development and launch phases.
It's important to note that prototyping often involves multiple iterations. You may go through several prototype phases, including alpha, beta, and pilot stages, each representing a step forward along the product roadmap and corresponding to an increasing score along the Technology Readiness Level scale.
Stage 4 – Build the product
With the design finalized and validated, the development phase begins. This is where the actual product is built, often using an iterative process that allows for continuous feedback and improvement. Design and development teams work closely together to ensure that all product components meet the required quality standards.
During development, the focus is on building the minimum viable product (MVP) first, allowing for early market introduction. Feedback from ongoing testing is integrated into each sprint, refining the product as it approaches launch readiness. Collaboration between development, design, and marketing teams ensures that the product is optimized for both functionality and customer satisfaction.
What is a minimum viable product? A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a basic version of a product that includes only the essential features needed to meet initial user needs and test the product in the market. It allows companies to launch quickly with minimal resources, gather feedback, and iterate on the product based on real user data. An MVP helps validate a product concept before committing to full-scale development
Stage 5 – Test and refine the product
The testing and refinement stage is crucial for ensuring that your product resonates with customers and stakeholders. This phase involves rigorous testing to ensure the product meets quality standards and fulfills customer requirements. Various testing methods can be employed, including:
- Alpha testing: Internal users evaluate product functionality and performance
- Beta testing: External users evaluate the product value proposition and overall customer satisfaction
- Pilot testing: A small group of customers or stakeholders evaluate the product's market response.
During this stage, it's essential to gather and analyze customer feedback to make ongoing improvements and inform future product development cycles. This iterative approach allows you to refine and improve your product based on real-world usage and customer insights.
Stage 6 – Launch and sell the product
The final stage of the product development life cycle is launch and commercialization. This phase involves introducing the product to the market and implementing it on your website. By this point, you should have finalized the design, quality tested your development and marketing strategy, and be ready to produce your final product.
A successful product launch requires systematic and well-coordinated execution. This includes developing a robust product launch strategy, creating a detailed product launch plan, and implementing a launch campaign to generate awareness, spark interest, create desire, and drive action.
Stage 7 – Collect feedback and improve the product
The product life cycle doesn’t end with the launch. Post-launch activities focus on gathering user feedback, analyzing market performance, and implementing continuous improvements. This phase is vital for maintaining product relevance and customer satisfaction over time.
By analyzing performance metrics and customer feedback, businesses can identify opportunities for enhancements or additional features. Ongoing iterations help extend the product’s life cycle and ensure that it remains competitive in the market. This phase also includes addressing any product-related issues that arise after launch.
How to Successfully Implement a PDLC
To make the most of your product development life cycle, you need to implement effective strategies that ensure success at every stage. Let’s take a look at some of the key approaches to help you manage product development and achieve great results.
Improve your cross-functional collaboration
One of the best ways to succeed in product development is through cross-functional collaboration. This means bringing together people from different departments to work as a team, creating a more well-rounded approach to solving problems and driving innovation. When everyone shares their knowledge and experience, you get higher-quality, more creative products.
With cross-functional teams, the product development process becomes more efficient. Instead of tasks moving from one department to another, the team works together from start to finish, ensuring better communication and faster decisions. This reduces delays and helps solve problems more quickly.
To build a strong cross-functional team, choose people with different skills who work well together. Good communication is key, so make sure team members are comfortable sharing their ideas and opinions. Set clear goals to keep everyone on the same page and focused on the same outcome.
Take advantage of agile methodologies
Using Agile methodologies in your product development life cycle is a game-changer when it comes to adapting to market interest and customer needs. Agile breaks down big projects into smaller, manageable tasks, focusing on speed, flexibility, and constant feedback.
In Agile software development, the process is split into sprints or iterations, usually lasting one to four weeks. During each sprint, cross-functional teams come together to plan, prioritize, and tackle the work. This approach helps you stay flexible, making it easy to adjust your development strategy based on changing requirements and feedback.
One of the biggest perks of Agile is delivering smaller, frequent product releases. This cuts down time to market, giving you a competitive edge. Plus, with testing at the end of each sprint, you can catch and fix problems early before they escalate.
Leverage customer feedback
Customer feedback is crucial to creating successful products. By regularly integrating user insights throughout the product development stage, you make sure your product actually meets their needs. This ongoing conversation between your product team and users turns development into a dynamic, customer-driven journey.
To get the most out of feedback, consider using a feedback-driven development (FDD) approach. This method puts customer input at the heart of your development strategy. By adding customer suggestions to your product backlog, you can prioritize features that matter most to the target audience.
Collecting feedback requires strong tools and channels like user surveys, feedback widgets, and analytics platforms. Real-time feedback lets you quickly solve issues and improve customer retention, making sure your marketing strategy and efforts align with what users truly want.
Conclusion
The product development life cycle is a roadmap for turning ideas into successful products. It helps businesses navigate the journey from concept testing to product launch, making sure the product meets market interest and customer needs. By breaking the process into stages and using strategies like cross-functional collaboration and Agile, companies can create products that stand out.
Staying flexible and listening to customer feedback throughout the product development stage is key. This allows companies to make informed decisions and build products people actually want. And remember, the work doesn’t stop at launch. Keep gathering feedback and improving to stay ahead in the fast-moving market. Mastering this process will help businesses drive growth and success.
FAQs
What are the 7 stages of a product development life cycle?
- The 7 stages are idea generation, screening, product concept development, business analysis, product design, testing, and commercialization. Each stage ensures the product development team follows a structured product development process, optimizing the product development cycle for successful market entry and growth.
What are the 4 stages of product life cycle growth?
- The 4 stages of product life cycle growth are introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. During the growth stage, the product development team works to increase market share while refining the product development cycle to sustain competitive advantage.
What is the PDLC process?
- The Product Development Life Cycle (PDLC) process refers to the end-to-end phases a product undergoes, from concept to market launch. It involves the product development team working on product concepts, designs, and iterations to meet market demands and increase market share.
What is the product life cycle?
- The product life cycle refers to the progression of a product through four key stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. It begins with the product's market launch and continues as it gains adoption, reaches peak sales, and eventually decreases in demand. Each stage impacts sales, revenue, and marketing strategies.
Read next:
- The 50 Most Common Product Manager Interview Questions (With Sample Answers) | Leland
- How to Develop Product Sense as a Product Manager | Leland
- The Most Common Technical Product Manager Interview Questions -- and How to Answer Them | Leland
- What is Product Management? | Leland
- How to Get Into Product Management (An Expert's Perspective) | Leland


















