Product Marketing Manager (PMM): The Ultimate Guide
Discover everything you need to know about being a Product Marketing Manager in this ultimate guide. Learn essential skills, responsibilities, and strategies to succeed as a PMM.
Posted March 6, 2025

Table of Contents
Ever wondered what a product marketing manager does? Think of it like this: you're the connection between the product team and the customers, making sure the product stands out and hits the mark. In this role, you're not just shaping how the product is seen, but also crafting messaging, analyzing market trends, and driving growth.
In this article, we'll dive into the essential skills and responsibilities of a product marketing manager. You'll learn about the key tasks involved in this role, from crafting compelling product messaging to analyzing market trends. We'll also explore how to become a product marketing manager, compare it to the role of a product manager, and highlight effective strategies for success in this field. Whether you're considering a career shift or looking to enhance your current PMM skills, this guide has got you covered.
Key Responsibilities & Skills of a Product Marketing Manager
PMM Responsibilities
As a product marketing manager (PMM), you play a crucial role in bridging the gap between product development and customer engagement. Your responsibilities are diverse and impactful, shaping the success of products in the market.
1. Market Intelligence
Gather and analyze data on customer needs, preferences, and trends to inform product strategies and ensure that offerings meet market demands. Advanced market research methodologies, such as surveys, interviews, and data analytics tools, are key to staying ahead of competitors.
2. Competitive Analysis
Research competitors to understand their strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning. Use competitive analysis frameworks like SWOT analysis or Porter’s Five Forces to identify opportunities for growth and areas where your product can differentiate.
3. Product Positioning and Messaging
Develop clear and compelling product positioning that communicates the unique value of your product. Craft messaging that resonates with target audiences, using real-world insights and customer personas to highlight the product’s benefits.
4. Go-to-Market Strategy
Plan and execute the product launch by outlining how the product will be introduced to the market, including target audience, marketing channels, and key milestones. Use detailed go-to-market frameworks and real-life case studies to ensure success.
5. Marketing Plan Development
Create comprehensive marketing team plans that align with business objectives. This includes defining goals, target audiences, tactics, timelines, and budgets to promote the product. Use market segmentation and customer insights to craft highly targeted plans.
6. Sales Enablement
Provide the sales team with the tools, training, and resources they need to effectively sell the product. This includes developing sales collateral, product demos, and competitive battle cards. Offer ongoing training and feedback loops to ensure sales are fully aligned.
7. Content Creation
Develop engaging, SEO-optimized content that educates and informs customers about the product. This includes blog posts, whitepapers, case studies, and social media posts. Tailor content to different stages of the buyer’s journey and optimize for conversions.
8. Campaign Management
Plan, execute, and manage cross-channel marketing campaigns to drive product awareness and engagement. Track campaign performance using KPIs like ROI, engagement rates, and conversion rates to optimize strategies based on data insights.
9. Performance Measurement
Track key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of marketing initiatives. Set measurable goals and use data from analytics tools like Google Analytics and Mixpanel to adjust strategies for continuous improvement.
10. Thought Leadership
Position your company or product as a leader in the industry by developing thought leadership content. This can include speaking at industry events, collaborating with influencers, or publishing in-depth reports. Establish credibility and trust with your audience by being the go-to expert in your field.
As a product marketing manager, your role is to deeply understand your target audience and their buying behaviors while keeping a pulse on competitive products and market dynamics. You work closely with product management and marketing teams to develop messaging that resonates with customers and clearly communicates the product’s value.
The PMM role demands a combination of strategic insight, creativity, and data-driven analysis to effectively communicate product value and drive growth.
PMM Skills
To excel as a PMM, you need a diverse set of skills that blend creativity, analytical thinking, and leadership. Here are some of the skills that will set you up for success in this highly dynamic role.
- Communication and Storytelling – As a PMM, you're the bridge between your product and its audience. You must be adept at crafting compelling narratives that resonate with your target market. This involves translating complex product features into relatable stories that highlight the benefits and value proposition. Your ability to communicate effectively across various channels and to different stakeholders is crucial.
- Strategic Thinking – Product marketing managers need to think strategically about the future of their products. This involves analyzing market trends, predicting customer needs, and aligning product development with business goals. You should be able to make decisions that balance risk and reward, always keeping the long-term success of the product in mind.
- Data Analysis – In today's data-driven world, PMMs must be comfortable working with numbers. You'll need to analyze product usage metrics, market research data, and user feedback to inform your strategies. This skill helps you make data-backed decisions and measure the success of your marketing output.
- Project Management – Launching a product or feature requires careful planning and coordination across multiple teams. As a PMM, you'll need to manage timelines, allocate resources, and ensure all stakeholders are aligned. Strong project management skills will help you keep launches on track and deliver results.
- Cross-functional Collaboration – Product marketing is a team sport. You'll work closely with product managers, engineers, designers, sales teams, and customer success managers. Your ability to foster collaboration, build relationships, and influence without direct authority is key to success in this role.
By honing these skills, you'll be well-equipped to tackle the challenges and opportunities that come with being a product marketing manager.
Bonus: What Tools Does a PMM Use?
Product Marketing Managers (PMMs) leverage a variety of tools to manage their diverse responsibilities, from conducting market research to executing campaigns and measuring performance. The specific tools a PMM uses will depend on their company, industry, and daily tasks. Generally, the tools fall into the following key categories:
Market Research and Analysis Tools
Understanding your customers and competitors is crucial to success. PMMs use these tools to gather insights, track trends, and analyze data that inform their product strategies:
- Typeform – Ideal for creating custom surveys and collecting detailed feedback from users.
- UserTesting – A platform for conducting usability tests and gathering real-time insights from actual users.
- Segment – A customer data platform that collects and organizes data for more targeted analysis.
- Amplitude – Provides detailed product usage analytics, helping PMMs track key metrics like engagement and retention.
Workflow and Project Management Tools
To coordinate cross-functional teams and keep projects on track, PMMs rely on tools that streamline workflow and communication:
- Trello – A simple, visual project management tool that helps PMMs organize tasks, track progress, and prioritize work across teams.
- Asana – A more robust project management tool that allows for tracking tasks, assigning responsibilities, and managing timelines.
- Slack – A communication hub that fosters real-time collaboration between team members, helping PMMs stay in sync with marketing, sales, and product teams.
- InVision – A collaborative design platform, especially useful for PMMs working closely with UX/UI teams to build and iterate on product prototypes.
- ProductBoard – Helps PMMs organize and prioritize feature ideas and feedback, translating insights into actionable product strategies.
- ProdPad – A product management and roadmapping tool that allows for effective backlog prioritization and feedback management.
Content Creation Tools
Creating engaging, high-quality content is essential for product marketing. These tools help PMMs design, produce, and distribute content that speaks to their audience:
- Canva – A user-friendly design tool for creating professional marketing materials such as presentations, social media graphics, and email campaigns.
- Sketch – A design tool primarily used for creating product prototypes and visual assets, especially in collaboration with design teams.
- Venngage – Great for designing infographics, reports, and data-driven content that can be shared internally or with external audiences.
- Wistia – A video hosting platform that enables PMMs to produce, manage, and track marketing videos with detailed performance analytics.
Marketing Automation and SEO Tools
To streamline marketing processes and optimize campaigns, PMMs need powerful tools for customer engagement, SEO, and email marketing:
- HubSpot – A comprehensive inbound marketing platform that supports content marketing, email campaigns, CRM, and analytics in one place.
- MailChimp – A leading email marketing tool that helps PMMs design, automate, and track email campaigns.
- Customer.io – A marketing automation tool that allows PMMs to send targeted messages based on customer behavior and activity data.
- Ahrefs – A robust SEO tool for keyword research, backlink analysis, and content optimization to improve organic search performance.
- BuzzSumo – A content research tool that helps PMMs identify trending topics, analyze competitors’ content, and discover key influencers for outreach.
Analytics and Performance Tracking Tools
Data is at the heart of any successful marketing strategy. These tools help PMMs measure the effectiveness of their campaigns, understand customer behavior, and optimize strategies:
- Google Analytics – A must-have tool for tracking website traffic, user behavior, and campaign performance metrics in real-time.
- Mixpanel – Focuses on tracking product usage and customer behavior, providing insights into how users engage with features.
- Klipfolio – A customizable dashboard tool for monitoring real-time marketing performance and visualizing key metrics from multiple data sources.
- Tableau – A powerful data visualization tool that allows PMMs to create interactive dashboards for analyzing product and marketing performance.
Product Marketing Manager vs. Product Manager
While both roles are crucial for a product's success, product marketing managers and product managers have distinct responsibilities and focus areas. Understanding these differences is key to fostering effective collaboration and achieving optimal results.
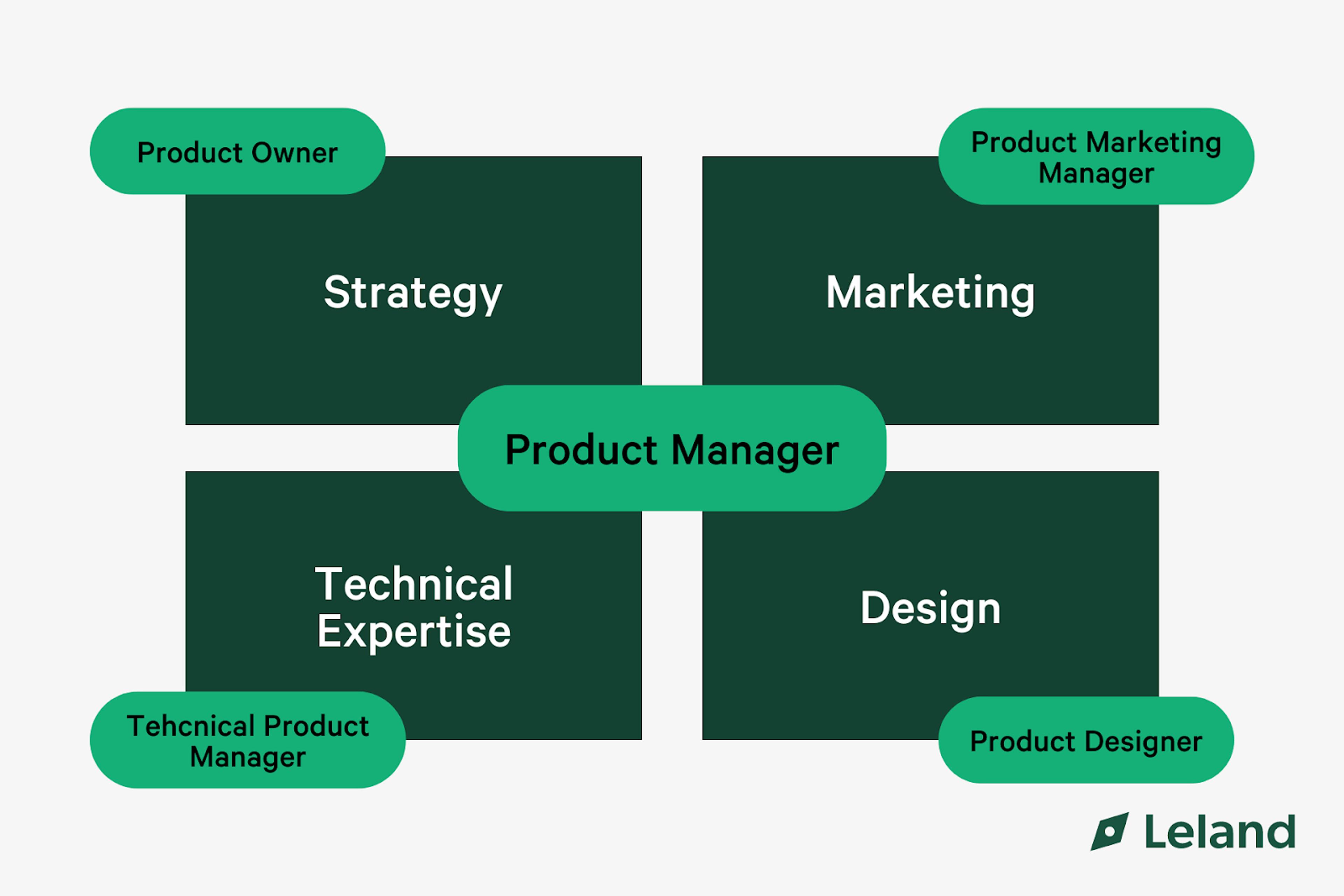
Key Differences
Product Managers
- Set goals based on customer needs, market analysis, and business objectives.
- Responsible for developing and defining the product by focusing on long-term success.
- Focus on problem-solving by understanding customer pain points and creating solutions.
- Own the product strategy and ensure it aligns with business goals.
- Develop and maintain the product roadmap, guiding the product’s future direction.
- Work closely with development teams to make sure the product is built according to plan.
Product Marketing Managers
- Voice of the customer: Product marketing managers ensure the product addresses customer needs and expectations.
- Lead the product's go-to-market strategy, coordinating product launches and promotions.
- Bridge between product development and market success by aligning teams on the product’s value.
- Communicate the product’s value through marketing materials and campaigns.
- Develop marketing campaigns to attract new prospects and customers.
- Ensure alignment of sales and marketing teams on product benefits and positioning.
Key Similarities
The key similarities between a Product Manager (PM) and a Product Marketing Manager (PMM) revolve around their shared goal of ensuring the success of a product in the market. Both a product manager and product marketing manager are deeply customer-focused, with PMs working to ensure the product addresses real user problems and PMMs focusing on positioning and communicating the product in a way that resonates with customers. Cross-functional collaboration is another area of overlap, as both PMs and PMMs work closely with teams such as engineering, design, sales, and marketing to align on product goals, timelines, and strategies.
Strategic thinking is crucial in both roles, although the focus varies: PMs concentrate on long-term product development strategies, while PMMs think strategically about how to position and launch products in the market. Data-driven decision-making also plays a significant role in each position, with PMs using data to analyze user feedback and prioritize features, and PMMs leveraging market research and performance metrics to fine-tune messaging and marketing efforts.
Both roles require strong problem-solving skills. PMs typically address technical and product-related challenges, while PMMs tackle issues related to positioning, marketing, and customer engagement. Ultimately, both PMs and PMMs are accountable for the product's success, with PMs ensuring the product meets user needs and PMMs ensuring it is effectively marketed to drive engagement and sales.
How They Work Together
Despite their distinct roles, PMs and PMMs form a complementary team that drives a product's success from inception to market adoption. They collaborate throughout the product life cycle, sharing insights and aligning their efforts to create products that resonate with customers.
For example, during the product's development phase, the PM leads the strategy and oversees progress, while the PMM learns about the product's strategy and customer personas to develop effective marketing tools and campaigns. This collaboration ensures that the product not only solves real customer problems but is also positioned effectively in the market.
| Pro Tip: Depending on the company, some PM positions include the PMM role. Make sure you’ve read the job description and understand what the specific job you’re applying to will entail. |
Curious to learn more? These additional resources will provide you insights about product management:
- What is Product Management?
- How to Develop Product Sense as a Product Manager
- Product Strategy Vs. Roadmap: What's the Difference and Why It Matters
- Selling Point: How to Position Your Product for Success
- Drive the Growth: Strategies for Effective Product Management
- An Overview of the Different Roles in Product Management
How to Become a Product Marketing Manager
Becoming a product marketing manager requires a combination of education, skills, and experience. Most companies expect candidates to have at least a bachelor's degree in marketing, business, or a related field (often indicated in their product marketing manager job description).
Gain Experience in Related Roles
Many Product Marketing Managers (PMMs) start their careers in adjacent fields such as marketing, product management, sales engineering, or consulting. Gaining experience in these areas helps build a strong foundation of relevant skills and insights. Look for opportunities to work on campaigns, technical projects, or strategic planning efforts. This exposure not only enhances your expertise but also demonstrates versatility and the ability to adapt to different challenges.
Develop Essential Skills
To succeed as a PMM, you need a diverse skill set. Focus on honing your communication, storytelling, content development, project management, collaboration, and analytical abilities. These skills are critical in shaping messaging, working with cross-functional teams, and making data-driven decisions. Continuously improving these areas will help you thrive in the fast-paced and multifaceted nature of product marketing.
Seek Hands-On Experience
Whenever possible, take on product marketing responsibilities within your current organization. Offer to collaborate on content creation or assist with events related to product launches. This proactive approach demonstrates your commitment to developing as a PMM and allows you to gain practical experience. Being hands-on not only builds your skillset but also helps you better understand the intricacies of product marketing.
Network and Learn
Networking is key to advancing in any field, and product marketing is no exception. Join product marketing groups and online communities, such as the Product Marketing Alliance Slack channel. These platforms provide valuable opportunities to connect with industry professionals, exchange ideas, and stay updated on the latest trends and best practices in product marketing.
Get Certified
Obtaining certifications in product marketing from reputable organizations is a great way to solidify your knowledge and enhance your credibility. Certifications show potential employers your dedication to mastering the field and staying current with the latest methodologies. Consider pursuing certifications in product marketing, digital marketing, or analytics to boost your qualifications.
Find a Mentor
Having a mentor can be invaluable as you navigate your career in product marketing. Seek out experienced product marketers who can provide guidance, share their experiences, and offer feedback on your work. A mentor can help you accelerate your learning curve and provide advice on overcoming challenges and seizing opportunities in the field.
Stay Curious and Proactive
Product marketing is a constantly evolving field, so staying curious and proactive is essential. Continuously educate yourself about marketing principles, market research techniques, and consumer behavior by taking online classes, reading professional blogs, and attending industry events. By staying informed and adaptable, you'll be better equipped to face new challenges and succeed in your role as a product marketing manager.
Product Marketing Manager Career Trajectory & Opportunities
As a product marketing manager, you have a dynamic career path with numerous growth opportunities. Your journey typically begins with a strong educational foundation. Most companies require at least a bachelor's degree, often in marketing, business, or a related field. While not mandatory, an MBA can provide an advantage, especially for roles in big tech companies. Business school can also be a great way to pivot into PM or PMM from another industry.
Experience is crucial in this field. You'll likely start in entry-level marketing or product management positions, building skills in areas like messaging, positioning, and market research. As you progress, you might move into roles such as product marketing specialist.
Read: The 25 Best Entry-Level Associate Product Management (APM) Programs (2024)
With experience, you can then advance to senior positions. The typical career progression includes titles like Senior Product Marketing Manager, Group Product Marketing Manager, Director, and eventually VP of Product Marketing. Some product marketing managers even transition into CMO roles, leveraging their strategic skills and cross-functional experience.
Product Marketing Manager Salary
Your salary expectations can vary based on experience and location. According to Glassdoor, the average salary for a product marketing manager in the U.S. is $113,439. However, salaries can range from $110,553 to $174,649, with most earning between $125,703 and $159,253.
The product marketing manager job offers flexibility for future career opportunities. You might transition into other marketing specializations, product management, or even explore opportunities in venture capital. The key is to identify the aspects of the job that challenge and motivate you, and seek roles that align with these interests while offering new learning opportunities.
What Does a Product Marketing Manager Actually Do?
As a product marketing manager, you play a crucial role in bridging the gap between product development and market success. Your core functions cover various aspects of bringing a product to market effectively. Let's explore some common product marketing manager responsibilities:
Market Analysis and Positioning
One of your primary tasks is to conduct thorough market research and analysis. This involves understanding your target audience, their needs, and pain points. You'll need to identify market trends, analyze competitors, and determine how your product fits into the larger landscape. With this information, you can develop a strong positioning strategy that differentiates your product from others in the market.
Messaging and Branding
Crafting compelling messaging is at the heart of the product marketing manager role. You'll need to translate complex product features into clear, customer-centric benefits. This involves developing a unique brand voice and creating messaging frameworks that resonate with your target audience. Your goal is to communicate the value proposition of your product effectively across various channels.
Product Launch Planning and Execution
A critical function of a PMM is to plan and execute a successful product launch. This involves coordinating with cross-functional teams, developing go-to-market strategies, and creating launch materials. You'll need to ensure that all aspects of the launch, from marketing campaigns to sales enablement, are aligned and executed flawlessly.
Sales Enablement
Supporting the sales organization is another crucial function. As a PMM, you'll create sales enablement materials, conduct training sessions, and provide the necessary tools and resources for the sales team to effectively sell your product. This includes developing product presentations, competitive battle cards, and other collateral that helps sales close deals.
Performance Tracking and Optimization
Finally, you'll need to measure the success of the marketing channels and campaigns, and optimize strategies accordingly. This involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), analyzing customer feedback, and continuously refining your approach based on data-driven insights. By monitoring performance, you can identify areas for improvement and ensure that your product marketing efforts are driving business growth.
How to Be an Effective Product Marketing Manager
As a product marketing manager, your role is crucial in driving product success. To excel in this position, you need to implement effective strategies that align with your company's goals and resonate with your target audience.
1. Identify your target audience
Understanding your target audience is the foundation of successful product marketing. Spend time conducting thorough market research to gain insights into your potential customers' needs, pain points, and motivations. Use social media, Google and Yelp reviews, and consumer insight tools to develop a robust understanding of your audience. This knowledge will help you craft marketing messages that truly resonate with your customers.
2. Make sure you have a clear value proposition
Your value proposition is what sets your product apart from competitors. It should clearly communicate why customers should choose your product over others. To create a compelling value proposition, focus on the specific solution your product provides and the unique benefits it offers to your target audience. Remember to keep it simple, honest, and easy to understand.
3. Choose the right marketing channels
Selecting the right marketing channels is crucial for reaching your audience effectively. Consider where your target customers spend their time online and which platforms they prefer for interacting with brands. Evaluate the effectiveness of different channels based on factors such as audience reach, engagement potential, and cost-effectiveness. A multi-channel approach can often yield the best results, allowing you to reinforce your message across various platforms.
4. Effectively allocate budget
Effective budget allocation is key to maximizing your marketing output. Allocate your budget based on where your audience is most likely to engage with your brand. Diversify your strategy to avoid putting all your eggs in one basket, and be prepared to adjust your budget allocation based on performance data. Remember to factor in costs for content creation, advertising, and tools or software needed for your marketing efforts.
5. Plan the timeline
Develop a clear timeline for your marketing activities, including product launches, campaigns, and sales kickoffs. Set specific deadlines for each step of your plan to keep your team accountable and ensure timely execution. Regular progress reviews will help you stay on track and make necessary adjustments along the way.
Conclusion
The role of a product marketing manager has a significant impact on a company's success, bridging the gap between product development and market adoption. From crafting compelling messaging to analyzing market trends, PMMs play a crucial part in ensuring products resonate with target audiences and drive business growth. Their diverse skill set, encompassing strategic thinking, communication, and data analysis, enables them to navigate the complex landscape of product launches and ongoing marketing efforts.
For those looking to pursue a career in product marketing management, the path offers exciting opportunities for growth and development. With a solid foundation in marketing principles and a willingness to adapt to changing market dynamics, aspiring PMMs can carve out a rewarding career. As the business world continues to evolve, the role of the product marketing manager remains essential, helping companies to innovate, communicate effectively, and stay ahead in competitive markets.
FAQs for Product Marketing Manager
What is a product marketing manager?
- A Product Marketing Manager is responsible for shaping how a product is perceived in the market. This includes crafting the messaging, defining the positioning, and establishing the branding. Additionally, they collect customer feedback, analyze it for improvements, and often play a role in post-launch customer engagement. Their ultimate goal is to guide potential customers through a journey, turning them from curious prospects into dedicated users.
What is the difference between a Product Manager and a Product Marketing Manager?
- A Product Manager focuses on product development, collaborating with the development team, while a Product Marketing Manager shapes the marketing strategy, positioning, and customer outreach. PMs drive the product life cycle, while PMMs handle the competitive landscape and messaging. Make sure to check the job description of the role you’re applying for.
What is the highest salary for a product marketing manager?
- The highest salary for a Product Marketing Manager can exceed $200,000, depending on industry, location, and experience level, particularly in competitive landscapes like tech.
What to major in to become a product marketing manager?
- Majoring in marketing, business administration, or communications helps develop the essential product marketing skills needed for this role, including marketing strategy and customer analysis.
What is the difference between product manager and product marketing?
- Product management focuses on product development, while product marketing ensures the marketing team effectively communicates the product’s value through strategies that meet customer needs.
What is the difference between PM and PMM responsibilities?
- Product Managers (PM) focus on product development and managing the roadmap, while Product Marketing Managers (PMM) concentrate on the marketing strategy, positioning, and competitive analysis.
What is the difference between a product marketer and a marketer?
- A product marketer focuses on a specific product, tailoring strategies to position it in the market, while a general marketing team member covers broader marketing responsibilities across various products or services.
What is the difference between a marketing manager and a production manager?
- A marketing manager develops strategies to promote products and grow market share, while a production manager oversees the manufacturing process to ensure products are produced efficiently.

















